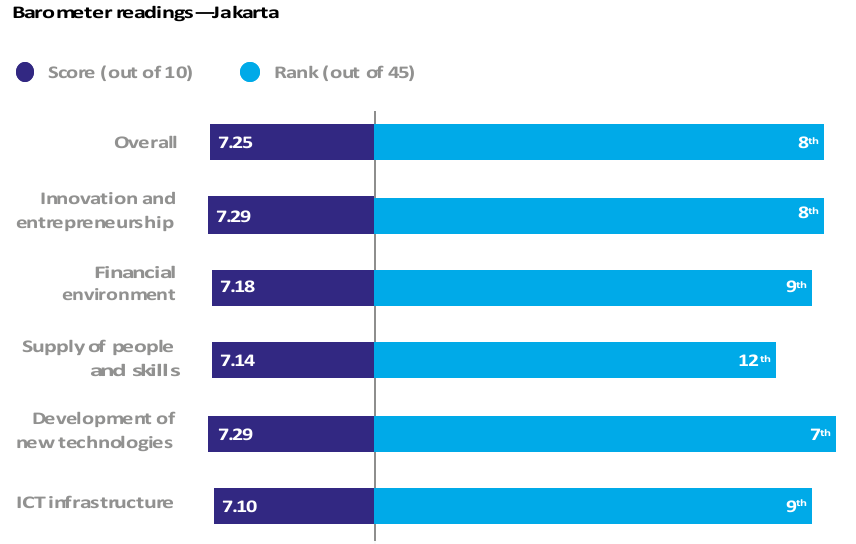
18 January 2018 – The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) has released a global research project commissioned by Telstra, a leading telecommunications and technology organisation and one of telkomtelstra’s parent companies, which assesses the confidence of business executives in their city’s environment and its conduciveness to supporting the digital ambitions of companies. It ranks Jakarta eighth out of 45 for overall business confidence.
The ‘Connecting Commerce’ report includes the first ever Digital Cities Barometer, a ranking of 45 cities around the world across five key categories relevant to business performance: innovation and entrepreneurship; the financial environment; people and skills; development of new technologies; and ICT infrastructure.
Erik Meijer, President Director of telkomtelstra, said the report reveals high levels of confidence in the world’s emerging economies, with Jakarta scoring in the top 10 across four out of the five research categories. Of the top 10 cities for overall confidence, seven are from developing Asian countries including Bangalore, Mumbai, New Delhi, Beijing, Manila and Shanghai. Conversely, lower confidence was recorded in developed cities such as Hong Kong and Tokyo.
“For digital transformation to be successful, it requires strong external support. It is therefore promising to see that business leaders in Jakarta are optimistic about their city’s ability to help unlock their organisation’s digital potential,” said Mr Meijer.
“Some of this optimism likely derives from the visible growth of Jakarta’s digital ecosystems, as well as the business-friendly national government that is serious about fostering digital entrepreneurship. Over the past 10 years, Indonesia, and Jakarta in particular, has seen good progress in the development of the digital business sector.”
“The results of this report show Jakarta’s position as the centre of the digital business ecosystem in Indonesia should not be underestimated, and we need to leverage this position to further accelerate Indonesia’s drive to reach its target of becoming a global digital economic hub by 2020,” said Mr Meijer.
While Jakarta performed well across all categories, the report found that 36 percent of Jakarta’s executives believe the supply of people and skills is the city’s toughest challenge.
“As businesses rapidly evolve to compete in the digital era, there is an increasing mismatch between university and technical institute curricula and the needs of companies. This has led to companies to recruit specialists from other countries in Southeast Asia and further afield. While this is not an issue specific to Indonesia, there is a clear need for the country’s education providers to focus on equipping students with relevant digital skills to complement Jakarta’s budding start-up environment.” Mr Meijer said.
Additional key findings from the research include:
- Jakarta’s executives are the world’s most complimentary of their government’s support, with 95 percent believing its municipal government will play a more positive role in developing the digital ecosystem over the next three years. However, more than half also think there is a current disconnect between the national and city governments when it comes to support for innovation.
- Digital security is the skill most in demand by businesses, with 41 percent of Jakarta-based executives listing it as the skill most needed to support digital transformation. At 25 percent, change management was named the second most important skill.
- Digital ecosystems in Jakarta are important. While 32 percent of Jakarta-based executives believe traditional structures such as business associations are a useful sources of assistance, informal communities and networks and innovation labs are also highly valued by businesses (both cited by 24 percent).
“It is evident that the pro-business agenda led by Indonesia’s national government since 2015 has delivered tangible and progressive outcomes to the city’s digital evolution. This type of strong government leadership should not be undervalued when 53 percent of survey respondents in Asian cities admitted they would be willing to relocate their operations to a city with a more favourable external environment,” Mr Meijer added.
“Organisations today have numerous options – both domestically and internationally – as to where they base their business operations. This report makes an important contribution to exploring what support executives need to digitally transform their business and thrive in a connected world,” said Mr Meijer.
“This research provides useful insights for the business community in Jakarta in understanding the challenges and opportunities that will drive further digital economic growth in Indonesia,” concluded Mr Meijer.
The full report, including the Digital Cities Barometer and the Indonesia country briefing, can be found at http://connectedfuture.economist.com/
END
Note to editors
The Connecting Commerce report includes the Digital Cities Barometer which is based on a survey of 2,620 executives in 45 cities conducted in June and July 2017. The list of cities includes 23 in Asia-Pacific, 19 in EMEA and three in North America. Eleven industries are represented, with the greatest numbers of respondents coming from professional services, financial services, manufacturing, retail and education. (No respondents were included from the telecommunications or technology sectors). C-level respondents account for 42% of the survey sample, with the balance being other senior executives.
************
Media Contact:
Abram Sakkan
Marketing Communication